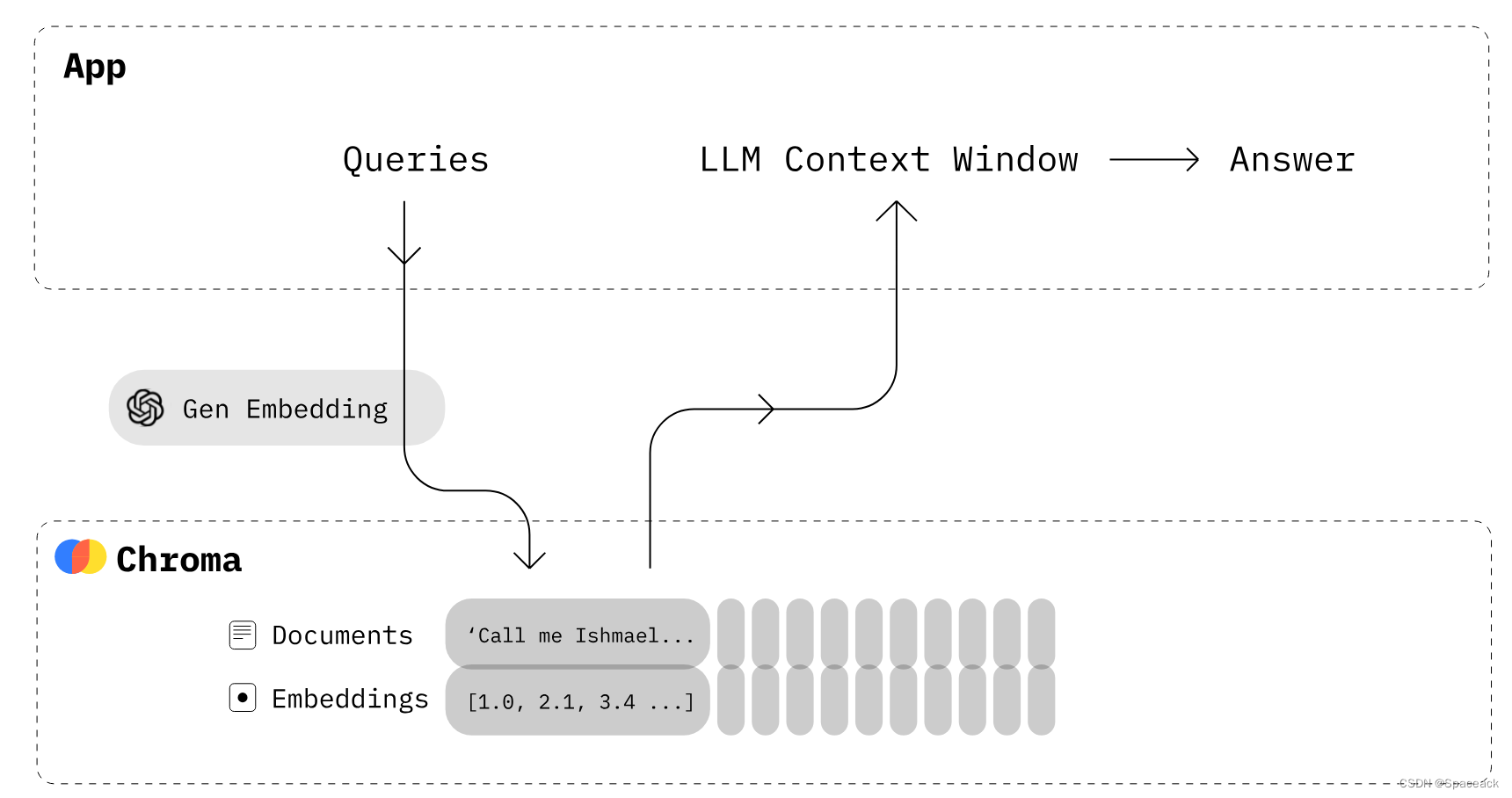
Chroma 是 AI 原生开源矢量数据库。Chroma 通过为 LLM 提供知识、事实和技能,使构建 LLM 应用程序变得容易。同时也是实现大模型RAG技术方案的一种有效工具。
先简单看看,整体数据处理流程:
1.创建 client,简单看成是初始化数据库
2.创建和选择 collection,简单看成是创建数据表
3.在当前 collection 下进行增删改查,以及相似度检索。简单看成对当前数据表进行增删改查
一、安装
pip install chromadb
二、client 的三种创建方式
方式一:直接创建 client
import chromadb client = chromadb.Client()
数据都存储在内存,程序运行完,数据会丢失
方式二:创建 client 时,设置数据持久化路径
client = chromadb.PersistentClient(path="/path/to/save/to")
client 会自动进行数据存储,当路径不存在时,会新建一个文件;当路径存在时,直接加载当前文件。
方式三:使用 client/server 方式,推荐使用
首先开启 chroma 服务,命令如下:
chroma run --path db_path
db_path 是你的数据存储路径。然后,创建 client
import chromadb chroma_client = chromadb.HttpClient(host='localhost', port=8000)
client 相关的接口
检查心跳:
client.heartbeat() # 单位为 nanosecond
清空数据库:
client.reset()
列出所有的 collection 列表:
client.list_collections()
三、collection 的使用
创建好了 client,接下来就是新建 collection。
collection 的命令规则:
1、名字长度必须限制在 3~63 个字符之间
2、名字必须以小写字母或数字开头和结尾,中间可以包含 点、破折号、下划线,不能包含两个连续的点
3、名字不能是一个有效的ip地址
3.1 创建 collection 相关的接口
创建一个 collection:
collection = client.create_collection(name="my_collection", embedding_function=emb_fn)
切换到一个 collection:
collection = client.get_collection(name="my_collection", embedding_function=emb_fn)
快捷创建方式:collection 存在时,直接加载使用;不存在时,则创建
collection = client.get_or_create_collection(name="test")
删除 collection:
client.delete_collection(name="my_collection")
3.2 创建 collection 的接口的相关参数说明
以 create_collection 为例,其它接口类似。
collection = client.create_collection(
name="collection_name",
metadata={"hnsw:space": "cosine"},
embedding_function=emb_fn
)
name:表示 collection 的名称
metadata:设置距离度量,{"hnsw:space": "cosine"} 表示使用的余弦距离,目前支持 "l2", "ip, 和 "cosine" 三种距离度量方式
l2:表示 squared L2 norm
ip:表示 Inner product
cosine:表示 Cosine similarity
embedding_function:提取嵌入表示的函数,默认支持 sentence-transformer 接口和相关模型,也支持自定义该函数。该参数默认为None,为 None 时,后续添加文本数据时,需要自己手动计算文本 embedding。不为 None,已经设置好嵌入模型时,后续直接添加文本数据即可,chroma 内部会自动计算 embedding。
注意:chroma 里检索时,返回的都是距离度量,值越小越相似,不要和相似性度量搞混了哟。3.3 collection 类相关的函数
返回 collection 下的前 10 条数据:
collection.peek()
返回 collection 包含的数据条目数:
collection.count()
修改 collection 名称:
collection.modify(name="new_name")
四、增删改查
创建好 collection 后,就可以在该 collection 下进行增删改查了。
4.1 添加文档
collection.add(
documents=["Article by john", "Article by Jack", "Article by Jill"],
embeddings=[[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]], metadatas=[{"author": "john"}, {"author": "jack"}, {"author": "jill"}],
ids=["1", "2", "3"])
documents:文档列表
embeddings:文档的嵌入表示。如果创建 collection 时,已经设置了embedding_function,则可以忽略该参数,内部会自动计算
metadatas:文档的元数据
ids:文档id。每个文档都有独一无二的id,当添加数据时,如果文档id重复,则后续id重复的数据都会跳过,不会覆盖之前的记录。4.2 删除文档
collection.delete(
ids=["1"],
where={"author": {"$eq": "jack"}}, # 表示 metadata 中 "author" 字段值等于 "jack" 的文档
where_document={"$contains": "john"}, # 表示文本内容中包含 "john" 的文档
)
ids:表示按照 文档id 删除
where:元数据过滤器,根据 metadata 中的字段进行过滤。后面详细介绍其语法规则
where_document:文本数据过滤器,根据文档内容进行过滤。后面详细介绍其语法规则
注意:ids,where,where_document 不能同时为空4.3 更新文档
collection.update(
documents=["Article by john", "Article by Jack", "Article by Jill"],
embeddings=[[10,2,3],[40,5,6],[70,8,9]],
metadatas=[{"author": "john"}, {"author": "jack"}, {"author": "jill"}],
ids=["1", "2", "3"])接口和添加文档接口一样,注意一下 ids 的值,如果某个 id 在数据库中不存在,不会影响已有 id 数据的更新。
4.4 同时更新和添加的接口
collection.upsert(
documents=["Article by john", "Article by Jack", "Article by Jill"],
embeddings=[[1,2,3],[2,5,6],[3,8,9]],
metadatas=[{"author": "john"}, {"author": "jack"}, {"author": "jill"}],
ids=["1", "2", "3"])加强了的更新接口,如果 id 在数据库中存在,则进行更新;如果不存在,则进行添加。
4.5 查询接口
collection.get(
ids=["1"],
where={"author": {"$eq": "jack"}}, # 表示 metadata 中 "author" 字段值等于 "jack" 的文档
where_document={"$contains": "john"}, # 表示文本内容中包含 "john" 的文档
)
ids:表示按照 文档id 查询
where:元数据过滤器,根据 metadata 中的字段进行过滤。后面详细介绍其语法规则
where_document:文本数据过滤器,根据文档内容进行过滤。后面详细介绍其语法规则
注意:ids,where,where_document 可以同时为空,如果都为空,则查询整个 collection 的数据4.6 相似文本检索接口
collection.query(
query_embeddings=[[1,2,3]],
# query_texts=["Article by john"],
n_results=3,
where={"author": {"$eq": "john"}}, # 表示 metadata 中 "author" 字段值等于 "jack" 的文档
where_document={"$contains": "john"}, # 表示文本内容中包含 "john" 的文档.
)
query_embeddings:可以直接提供文本的嵌入,检索数据库中最相似的文本。一般不常用。
query_texts:待检索的文本
n_results:返回最相似的记录的条数
where:同上,注意过滤的顺序,chroma 里是先进行过滤,然后在过滤后的数据上进行相似度计算。
where_document:同上,注意过滤的顺序,chroma 里是先进行过滤,然后在过滤后的数据上进行相似度计算。
注意:query_embeddings 和 query_texts 不能同时使用,只能选取其中一个。4.7 where 语法
where 过滤器是针对元数据 metadata 的,语法格式如下:
{
"metadata_field": {
<Operator>: <Value>
}
}
其中支持的 Operator 算子包含:
$eq - 等于 (string, int, float)
$ne - 不等于 (string, int, float)
$gt - 大于 (int, float)
$gte - 大于等于 (int, float)
$lt - 小于 (int, float)
$lte - 小于等于 (int, float)
$eq 算子有个特殊的简写方式
{
"metadata_field": "search_string"
}
等价于
{
"metadata_field": {
"$eq": "search_string"
}
}
如果 where 中的 key 在元数据metadata中不存在,程序运行不会报错,只是返回空数据
where 还支持包含操作符 $in 和 $nin,语法格式如下
{
"metadata_field": {
"$in": ["value1", "value2", "value3"]
}
}
$in - metadata_field字段的值在预定义的列表里 (string, int, float, bool)
$nin - metadata_field字段的值不在预定义的列表里 (string, int, float, bool)4.8 where_document 语法
where_document 过滤器是针对文本内容的
chroma 中提供了两种操作符,$contains and $not_contains,格式如下:
{
"$contains": "search_string"
}
表示检索的文本中包含 search_string 关键词
{
"$not_contains": "search_string
}
表示检索的文本中不包含 search_string 关键词4.9 逻辑运算符
逻辑操作符包含 $and 和 $or,语法如下
{
"$and": [
{
"metadata_field": {
<Operator>: <Value>
}
},
{
"metadata_field": {
<Operator>: <Value>
}
}
]
}
$and:表示要满足列表中的所有过滤条件
$or:表示只需满足列表中的任一过滤条件where 和 where_document 都支持逻辑运算符
五、demo
5.1 创建 collection
import chromadb
# 一、创建客户端client = chromadb.PersistentClient(path="./vector_store")
# 二、创建 collection
client.delete_collection(name="test")
collection = client.get_or_create_collection(name="test",
metadata={"hnsw:space": "cosine"}) # 目前支持 cosine,ip,l2 三种距离,默认为 l2 距离5.2 添加文档
collection.add(
documents=["Article by John", "Article by Jack", "Article by Jill"],
embeddings=[[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]],
metadatas=[{"author": "john"}, {"author": "jack"}, {"author": "jill"}],
ids=["1", "2", "3"])
collection.get()打印结果:
{'ids': ['1', '2', '3'],
'embeddings': None,
'metadatas': [{'author': 'john'}, {'author': 'jack'}, {'author': 'jill'}],
'documents': ['Article by John', 'Article by Jack', 'Article by Jill'],
'uris': None,
'data': None}5.3 查询文档
collection.get(
# ids=["1"],
# where={"author": {"$eq": "jack"}}, # 表示 metadata 中 "author" 字段值等于 "jack" 的文档
# where_document={"$contains": "john"}, # 表示文本内容中包含 "john" 的文档
)5.4 检索相似性文档
collection.query(
query_embeddings=[[1,2,3]],
# query_texts=["Article by john"],
n_results=3,
where={"author": {"$in": ["john", "jack"]}}, # 表示 metadata 中 "author" 字段值在列表 ["john", "jack"] 里的文档
where_document={"$or": [{"$contains": "John"},{"$contains": "Jack"}]}, # 表示文本内容中包含 "John" 的文档或包含 "Jack"的文档
)输出结果:
{'ids': [['1', '2']],
'distances': [[0.0, 0.025368153802923787]],
'metadatas': [[{'author': 'john'}, {'author': 'jack'}]],
'embeddings': None,
'documents': [['Article by John', 'Article by Jack']],
'uris': None,
'data': None}可以自行修改 where 和 where_document 过滤器,查看过滤规则的作用方式
六、embedding
创建 collection 时,可以自定义 embeddding 函数,这里以 huggingface transformer 包为例,来加载个最近出来的 bge 模型。
import chromadb
from chromadb import Documents, EmbeddingFunction, Embeddings
from chromadb.utils.embedding_functions import (
SentenceTransformerEmbeddingFunction
)
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModel
import torch
class MyEmbeddingFunction(EmbeddingFunction):
def __init__(self, model_name, device="cpu") -> None:
self.model_name = model_name
self.tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)
self.model = AutoModel.from_pretrained(model_name)
self.device = torch.device(device)
self.model.to(self.device)
@staticmethod
def mean_pooling(model_output, attention_mask): token_embeddings = model_output[0] # First element of model_output contains all token embeddings
input_mask_expanded = attention_mask.unsqueeze(-1).expand(token_embeddings.size()).float()
return torch.sum(token_embeddings * input_mask_expanded, 1) / torch.clamp(input_mask_expanded.sum(1), min=1e-9)
def __call__(self, input: Documents) -> Embeddings:
encoded_input = self.tokenizer(list(input), padding=True, truncation=True, return_tensors='pt').to(self.device)
# print(encoded_input)
with torch.no_grad():
model_output = self.model(**encoded_input)
if "bge" in self.model_name.lower():
sentence_embeddings = model_output[0][:, 0]
else:
sentence_embeddings = self.mean_pooling(model_output, encoded_input['attention_mask'])
sentence_embeddings = torch.nn.functional.normalize(sentence_embeddings, p=2, dim=1)
return sentence_embeddings.cpu().numpy().tolist()
# GanymedeNil_text2vec-large-chinese 模型
collection = client.create_collection(
name=name,
metadata={"hnsw:space": "cosine"},
embedding_function=MyEmbeddingFunction(model_name="GanymedeNil_text2vec-large-chinese", device="cpu")
)
# bge-base-zh-v1.5 模型
collection = client.create_collection(
name=name,
metadata={"hnsw:space": "cosine"},
embedding_function=MyEmbeddingFunction(model_name="bge-base-zh-v1.5", device="cpu")
)使用 huggingface 上的 bge-base-zh-v1.5 或 GanymedeNil_text2vec-large-chinese 模型,自定义了一个基于huggingface transformer包的接口。实在不想折腾 sentence-transformer 包了,虽然 chroma 默认支持的是该包,但 sentence-transformer 不同版本的兼容性以及和 pytorch 版本的严格对齐要求,让人有点劝退。